Great Boiling Spring: Difference between revisions
Moved Borax to another section |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
An April 29, 1912 newspaper article states that "Borax" in the water at [[Trego]] was the cause of a train engine boiler explosion that killed three people at [[Antelope]]. | An April 29, 1912 newspaper article states that "Borax" in the water at [[Trego]] was the cause of a train engine boiler explosion that killed three people at [[Antelope]]. | ||
== History == | |||
The December 7, 1941 (Pearl Harbor Day) Nevada State Journal reports that Leslie E. Johnson transferred a deed to Charlie Wibel and H.J. Hughes for T32N, R23E, Sec. 10 and 15. Section 15 is Gerlach, Section 10 is north of Gerlach, so this could be the springs. Wibel also owned a gun club near [[Winnemucca Lake]]. | The December 7, 1941 (Pearl Harbor Day) Nevada State Journal reports that Leslie E. Johnson transferred a deed to Charlie Wibel and H.J. Hughes for T32N, R23E, Sec. 10 and 15. Section 15 is Gerlach, Section 10 is north of Gerlach, so this could be the springs. Wibel also owned a gun club near [[Winnemucca Lake]]. | ||
Revision as of 05:55, 24 November 2014
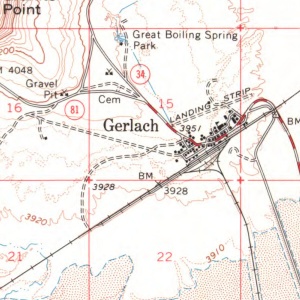
The Gerlach "Great Boiling" Springs are located less than a mile west of Gerlach.
The name "Great Boiling Spring" comes from "'"Map of an Exploring Expedition to the Rocky Mountains in the Year 1842 - Oregon and Northern California in the years 1843-44,' Baltimore, MD: no publication date, no scale given. Litho by E. Weber & Co. Prepared by Brevet Capt. J.C. Fremont of the Corps of Topographical Engineers under the control of Col. J.J. Abert, Chief of the Topographical Bureau." (Citation from GNIS). See also Fremont's 1842 map (David Rumsey)
- Alternative names:
- Boiling Springs: Bancroft's Map of California and Nevada: 1868, scale 1 inch=24 miles. H. H. Bancroft & Co., Booksellers & Stationers, San Francisco, Calif. Entered according to an act of Congress, A.D. 1868, by H. H. Bancroft & Company in the Clerk's Office of the District Court of the United States for the Northern District of California.
- Borax Hot Springs: Clason's Map of Nevada. Denver: Clason Map Company, 1916, scale 1 in=16 miles
- See Borax below.
- Gerlach Hot Springs: Carlson, Helen S., "Nevada Place Names, A Geographical Dictionary," Reno, Nevada: University of Nevada Press, 1974, 282 pp
- Mud Springs: Garside, L. J. and Schilling, J. H. "Thermal Waters of Nevada," Reno: Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Bulletin 91, 1979, 163 pp. Describes hot springs and hot water seeps of Nevada with location information and map at 1:1,000,000. map. (Mud Springs refers to the springs on the other size of Highway 447, see "Garside (1979) Aerial Photo," (archive.org)).
- Great Boiling Spring Park: Note that this is a historical name and that there is no public park
- Source: Gerlach (1964, Rp. 1977), Nevada 1:62,500 topographic quadrangles. (see thumbnail)
- GNIS. Citation: "U.S. Geological Survey. Geographic Names Phase I data compilation (1976-1981). 31-Dec-1981. Primarily from U.S. Geological Survey 1:24,000-scale topographic maps (or 1:25K, Puerto Rico 1:20K) and from U.S. Board on Geographic Names files. In some instances, from 1:62,500 scale or 1:250,000 scale maps." Date added: 12-Dec-1980
Borax
Garside states:"It has been reported that a borax works operated for a short time at Gerlach Hot Springs, but Papke (1976)[1] believes that this information is probably not true. There is not a large amount of boron in the spring water, and no borates can be found at the site."[2]
A 1912 reference states: "Hot Springs waters at Gerlach Washoe County Nev Borax plant established at one time"[3]
Another 1912 reference states: "Some other deposits of this type were operated in a small way at this time including a small plant established at the Hot Springs near the present site of the town of Gerlach, in Washoe County Nev., when this place was still some hundred miles more or less from its nearest railroad shipping point[4]
In 1965, Cromwell wrote that an unpublished memorandum by H.S. Gale states that in the 1890's (before the railroad) 3000 tons of Borax were shipped[5].
An April 29, 1912 newspaper article states that "Borax" in the water at Trego was the cause of a train engine boiler explosion that killed three people at Antelope.
History
The December 7, 1941 (Pearl Harbor Day) Nevada State Journal reports that Leslie E. Johnson transferred a deed to Charlie Wibel and H.J. Hughes for T32N, R23E, Sec. 10 and 15. Section 15 is Gerlach, Section 10 is north of Gerlach, so this could be the springs. Wibel also owned a gun club near Winnemucca Lake.
In 1973, Deborah Ann Brockelsby (age 19) from Lake Tahoe was scalded to death in one of the small pools (Reno Evening Gazette March 23, 1973, see also March 19 and 20). It was reported that she dove in to a hot pool after mistaking it for the cold pool. The pools were separated by a walkway. Merced Sun-Star - Mar 19, 1973.
In "Assessment of Geothermal Resources of the United States (1975, USGS)", Gerlach was listed as having a surface temperature of 86C.
Gerlach Green Energy and U.S. Geothermal hold geothermal leases near the springs.
Gerlach Bath House
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Gerlach Geothermal: "Great Boiling Springs were used extensively for bathing for many years ( figure). Some pools are too hot for swimming; a 19-year-old woman was scalded to death in one of these in 1973, an indication of the danger inherent in geothermal areas. The Gerlach General Improvement District built a bath house using geothermal fluids in 1989. The facility was planned for use by tourists and local residents. The facility has been unable to obtain a permit from the health department because of plugging of water filters by sediment from the well. No bathing facilities are available at the present (2002)."
- Image of Gerlach Bath House (1994)
References
- ↑ K. G. Papke, (1976) Evaporites and brines in Nevada playas: Nevada Bur. Mines and Geol. Bull. 87.
- ↑ L. J. Garside and J. H. Schilling, "Thermal Waters of Nevada," Reno: Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Bulletin 91, 163 pages, 1979.
- ↑ Mineral Resources of the United States, Part 2," p. 840-841, 1912.
- ↑ Minerals Yearbook," p. 858, 1912.
- ↑ H. R. Cromwell, "B065: Mineral and water resources of Nevada," NV Bureau of Mines & Geology.
External Resources
- Gerlach Hot Springs Park (Wikipedia)
- GNIS Great Boiling Springs [http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gazpublic/getgooglemap?p_lat=40.6615681&p_longi=-119.3660202&fid=856518 Google Maps
- Donald E. White, "Violent mud-volcano eruption of Lake City hot springs, northeastern California", Geol. Soc. America Bull., v. 66, no.9, p.1109-1130, 1955. Mud volcanoes are mentioned near Gerlach "Great Boiling" Springs.
- L.J Garside and J.H. Schilling. 1979. "Thermal waters of Nevada." Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Bulletin 91. 1979
- Gerlach Geothermal (Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology)
- University of Georgia Great Boiling Springs (Dead Link)
- Brian P. Hedlund Summer 2006 Nevada Hot Springs (Dead Link)
"The goals of this trip were to obtain high quality chemistry data, particularly redox active species, and samples for 16S rDNA clone library construction. The chemistry data will be used to model which chemolithotrophic metabolisms are most favorable in the bulk water at the sampling site and the clone libraries will allow us to see which microorganisms are present near the sediment/water interface at each site. We also helped Chuanlun Zhang with an experiment designed to enrich for microorganisms with chemolithotrophic activities of interest in situ."
- Nevada State Journal, "Gerlach News, March 14, 1926, p. 2. Meeting held at the courthouse to discuss "possible big improvements" to the hot springs.
- Nobles Trail (Emigrant Trails West) "Great Boiling Springs - Marker N-7"
- Robert Sanders, "Hot springs microbe yields record-breaking, heat-tolerant enzyme," 5-Jul-2011, UC Berkeley. A bacterium was found in the Gerlach Hot Springs that breaks down cellulose at temperatures near the boiling point of water. Image of the springs is included.
Images
- "Double Hot Springs boiling water. 0.8 miles north of Gerlach, Washoe County. 17 May 1946," UNRS-P1988-55-0736, J. A. Carpenter Collection, Special Collections Department, University of Nevada, Reno Libraries. Note that "Double Hot Springs" is actually elsewhere.
- WA-914, "Gerlach, 1964," Nevada Historical Society. View of the springs looking north east towards Old Razorback Mountain.
- WA-915, "Great Boiling Springs Park, Springs Discovered and named by John C. Fremont 1844. Park being developed by Gerlach-Empire Lions Club," 1964, Nevada Historical Society. Picture of the sign for the springs. Note that the plural, "Springs," is used, not the singular that is on the map.